Java language has many useful features but the primary goal behind its (Java) creation was to enhance the portability and security of a computer language. Please find all important Java features below.
Java features:
1. Familiar:
Java is familiar because its syntax is based on C++.
2. Simple and Easy:
Java is easy to learn and simple because:
- There is no use for header files in Java.
- Completed and Rarely used features are eliminated i.e. the use of a pointer, operator overloading, etc.
2. Platform Independent:
Write once, run anywhere (WORA).
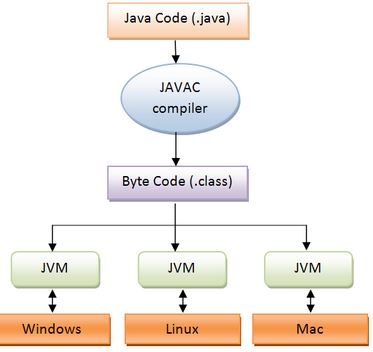
“Java Platform Independence,” and it is also called “Write Once, Run Anywhere” (WORA). It is a fundamental feature of the Java programming language. It means that Java code can be written once and executed on various computing platforms. Java Compiler compiles the Java code and converts it into bytecode. This bytecode can be run on multiple platforms with the help of JVM.
3. Object-Oriented:
Java is Object-oriented throughout the language- i.e. no coding outside of class definitions. Everything in Java is an Object.
The basic concepts of OOPs are given below.
- Object
- Class
- Encapsulation
- Abstraction
- Inheritance
- Polymorphism
4. Robust:
The dictionary meaning of Robots is solid and healthy.
Java is robust because of the following:
- Java has a Built-in Exception handling feature.
- Java first checks the reliability of the code before Execution etc.
- Strong type checking. It means all data must be declared an explicit type.
- All local variables in Java must be initialized.
- Automatic garbage collection.
5. Secure:
We can create virus-free applications in Java and that’s why it is best known for its security. Java is secure because it provides:
- With the help of access modifiers (public, private, etc.), java provides access restrictions.
- Byte code verification – It checks classes after loading.
- Class loader – It confines objects to unique namespaces.
- Security manager – What resources a class can access in Java are determined by the Security Manager. These include operations like reading and writing to the local disk.
6. Distributed:
In Java, we can create distributed applications that’s why Java is distributed. Java provides the facility so that programs can be accessed remotely from any network computer rather than writing programs on the local computer. FTP and HTTP protocols are developed in Java.
Note: Network connections in Java, are very much easy as compared to C/C++.
7. Compiled and interpreted:
Java code is translated into bytecode after compilation and is interpreted by JVM (Java Virtual Machine). This two steps process provides extensive code-checking feature and increase security.
8. Portable:
The dictionary meaning of Portable is “that can be moved or carried easily”. WORA – Write once, run anywhere feature makes it portable.
9. Architecture-Neutral:
Java code is translated into bytecode after compilation. This bytecode is which is independent of any computer architecture and only needs JVM (Java Virtual Machine) to execute.
10. High performance:
JVM can execute bytecode (highly optimized) very fast. JVM will use the Just in Time (JIT) compilation technique to execute bytecode.
11. Code Re-usability:
Java provides the code re-usability With the Help of Inheritance.
12. Multithreading:
Java provides a multitasking feature with the help of lightweight processes called threads.
13. Dynamic:
Java has the mechanism of linking dynamic new classes, objects, and methods.
Please also read the New Java 7 & Java 8 features.
