To capture the pictures and videos, the camera is used. To control a camera in Android, the methods of the camera API are used. To work on camera in Android, we can choose either of the ways mentioned below:
- By Camera Intent
- By Camera API
Understanding basic classes of Camera Intent and API:
The Camera Intent and API have many classes. We are going to discuss some important classes of the Camera Intent and API.
Intent:
To capture pictures and videos without using the instance of Camera class, the below constants of MediaStore class can be used.
- ACTION_IMAGE_CAPTURE
- ACTION_VIDEO_CAPTURE
Camera:
The pictures and videos are taken using the main class of camera API, i.e., Camera.
SurfaceView:
The surface view or a preview of the live camera is represented by the SurfaceView class.
MediaRecorder:
To record videos using a camera or to record audio files, the MediaRecorder class is used in Android.
Example: Android camera app by camera intent:
In the below example, we are using the Camera Intent to capture an image using the camera. The image is then displayed using the ImageView.
activity_main.xml:
In the activity_main.xml file, we will drag an ImageView and a button from the palette.
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?> <RelativeLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="match_parent" tools:context=".MainActivity" > <Button android:id="@+id/button1" android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:layout_alignParentBottom="true" android:layout_centerHorizontal="true" android:text="Open Camera" > </Button> <ImageView android:id="@+id/imageView1" android:layout_width="fill_parent" android:layout_height="fill_parent" android:layout_above="@+id/button1" android:layout_alignParentTop="true" android:src="@mipmap/ic_launcher" > </ImageView> </RelativeLayout> |
Activity class:(File: MainActivity.java)
In the MainActivity.java file, we will write the code to capture images using the camera. We will also add the code to display the image on the image view.
package com.example.radioapp; import android.app.Activity; import android.content.Intent; import android.graphics.Bitmap; import android.os.Bundle; import android.view.View; import android.widget.Button; import android.widget.ImageView; public class MainActivity extends Activity { private static final int CAMERA_REQUEST = 1888; ImageView imageView; public void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) { super.onCreate(savedInstanceState); setContentView(R.layout.activity_main); imageView = (ImageView) this.findViewById(R.id.imageView1); Button photoButton = (Button) this.findViewById(R.id.button1); photoButton.setOnClickListener(new View.OnClickListener() { @Override public void onClick(View v) { Intent cameraIntent = new Intent(android.provider.MediaStore.ACTION_IMAGE_CAPTURE); startActivityForResult(cameraIntent, CAMERA_REQUEST); } }); } protected void onActivityResult(int requestCode, int resultCode, Intent data) { if (requestCode == CAMERA_REQUEST) { Bitmap photo = (Bitmap) data.getExtras().get("data"); imageView.setImageBitmap(photo); } } } |
AndroidManifest.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?> <manifest xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" package="com.example.radioapp"> <uses-permission android:name="android.permission.CAMERA" /> <application android:allowBackup="true" android:icon="@mipmap/ic_launcher" android:label="@string/app_name" android:theme="@style/AppTheme" > <activity android:name=".MainActivity" android:label="@string/app_name" > <intent-filter> <action android:name="android.intent.action.MAIN" /> <category android:name="android.intent.category.LAUNCHER" /> </intent-filter> </activity> </application> </manifest> |
Output 1:
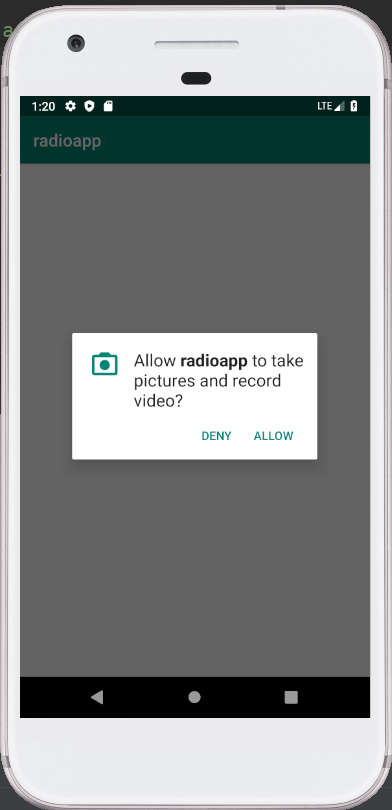
Output 2:

Output 3:
