The LinkedList class extends AbstractSequentialList and implements the List and Deque interface. It uses a linked list data structure to store elements. It can contain duplicate elements. It is not synchronized.
Note:
- It does not provide a random access facility.
- No shifting needs to occur in the Java LinkedList class, thus manipulation is fast.
Doubly Linked List:
Elements can be added or removed elements from both sides in a doubly-linked list.
LinkedList class declaration:
Declaration for java.util.LinkedList class:
public class LinkedList<E> extends AbstractSequentialList<E> implements List<E>, Deque<E>, Cloneable, Serializable
Java LinkedList Constructors:
| Constructor | Description |
| LinkedList() | It will create an empty list. |
| LinkedList(Collection<? extends E> c) | It will create a list containing the elements of the specified collection. In the same order, as they are returned by the collection’s iterator. |
Java LinkedList Methods:
| Method | Description |
| boolean add(E e) | It will append the specified element to the end of a list. |
| void add(int index, E element) | It will insert the specified element at the specified position index in a list. |
| boolean addAll(Collection<? extends E> c) | It will append all of the elements in the specified collection to the end of this list, in the order that they are returned by the specified collection’s iterator. |
| boolean addAll(Collection<? extends E> c) | It will append all of the elements in the specified collection to the end of this list, in the order that they are returned by the specified collection’s iterator. |
| boolean addAll(int index, Collection<? extends E> c) | It will append all the elements in the specified collection, starting at the specified position of the list. |
| void addFirst(E e) | It will insert the given element at the beginning of a list. |
| void addLast(E e) | It will append the given element to the end of a list. |
| void clear() | It will remove all the elements from a list. |
| Object clone() | It will return a shallow copy of an ArrayList. |
| boolean contains(Object o) | It will return true if a list contains a specified element. |
| Iterator<E> descendingIterator() | It will return an iterator over the elements in a deque in reverse sequential order. |
| E element() | It will retrieve the first element of a list. |
| E get(int index) | It will return the element at the specified position in a list. |
| E getFirst() | It will return the first element in a list. |
| E getLast() | It will return the last element in a list. |
| int indexOf(Object o) | It will return the index in a list of the first occurrence of the specified element, or -1 if the list does not contain any element. |
| int lastIndexOf(Object o) | It will return the index in a list of the last occurrence of the specified element, or -1 if the list does not contain any element. |
| ListIterator<E> listIterator(int index) | It will return a list-iterator of the elements in proper sequence, starting at the specified position in the list. |
| boolean offer(E e) | It will add the specified element as the last element of a list. |
| boolean offerFirst(E e) | It will insert the specified element at the front of a list. |
| boolean offerLast(E e) | It will insert the specified element at the end of a list. |
| E peek() | It will get the first element of a list. |
| E peekFirst() | It will get the first element of a list or returns null if a list is empty. |
| E peekLast() | It will get the last element of a list or returns null if a list is empty. |
| E poll() | It will get and eliminate the first element of a list. |
| E pollFirst() | It will get and eliminate the first element of a list or returns null if a list is empty. |
| E pollLast() | It will get and eliminate the last element of a list or returns null if a list is empty. |
| E pop() | It will pop an element from the stack represented by a list. |
| void push(E e) | It will push an element onto the stack represented by a list. |
| E remove() | It will get and eliminate the first element of a list. |
| E remove(int index) | It will eliminate the element at the specified position in a list. |
| boolean remove(Object o) | It will eliminate the first occurrence of the specified element in a list. |
| E removeFirst() | It will eliminate and return the first element from a list. |
| boolean removeFirstOccurrence(Object o) | It will eliminate the first occurrence of the specified element in a list (when traversing the list from head to tail). |
| E removeLast() | It will eliminate and return the last element from a list. |
| boolean removeLastOccurrence(Object o) | It will eliminate the last occurrence of the specified element in a list (when traversing the list from head to tail). |
| E set(int index, E element) | It will replace the element at the specified position in a list with the specified element. |
| Object[] toArray() | It will return an array containing all the elements in a list in proper sequence (from first to the last element). |
| <T> T[] toArray(T[] a) | It will return an array containing all the elements in the proper sequence (from first to the last element); the runtime type of the returned array is that of the specified array. |
| int size() | It will return the number of elements in a list. |
LinkedList example:
LinkedListTest.java
import java.util.Iterator; import java.util.LinkedList; /** * This class is used to show the LinkedList functionality. * @author w3schools */ public class LinkedListTest { public static void main(String args[]){ //Create LinkedList object. LinkedList linkedList = new LinkedList(); //Add objects to the HashSet. linkedList.add("Amani"); linkedList.add("Prabhjot"); linkedList.add("Nidhi"); linkedList.add("Vandana"); linkedList.add("Poonam"); //Size of the LinkedList object. System.out.println("Size: " + linkedList.size()); //Print the LinkedList object. System.out.println("LinkedList elements:"); System.out.println(linkedList); //Print the LinkedList elements using iterator. Iterator iterator1=linkedList.iterator(); System.out.println("LinkedList elements " + "using iterator:"); while(iterator1.hasNext()){ System.out.println(iterator1.next()); } //Add an object at the specific position. linkedList.add(2,"Jagdeep"); //Remove a element from a specific position. linkedList.remove(3); //Remove last element. linkedList.removeLast(); //Size of the LinkedList object. System.out.println("Size after manipulation: " + linkedList.size()); //Print the LinkedList object. System.out.println("LinkedList elements " + "after manipulation:"); System.out.println(linkedList); //Print the LinkedList elements using iterator. Iterator iterator2=linkedList.iterator(); System.out.println("LinkedList elements after " + "manipulation using iterator:"); while(iterator2.hasNext()){ System.out.println(iterator2.next()); } } } |
Output:
Size: 5 LinkedList elements: [Amani, Prabhjot, Nidhi, Vandana, Poonam] LinkedList elements using iterator: Amani Prabhjot Nidhi Vandana Poonam Size after manipulation: 4 LinkedList elements after manipulation: [Amani, Prabhjot, Jagdeep, Vandana] LinkedList elements after manipulation using iterator: Amani Prabhjot Jagdeep Vandana |
Example: Different ways to add elements:
import java.util.*; public class LinkedListExample{ public static void main(String args[]){ LinkedList<string> ll=new LinkedList</string><string>(); System.out.println("Initial list of elements: "+ll); ll.add("A"); ll.add("B"); ll.add("C"); System.out.println("After invoking add(E e) method: "+ll); //Adding an element at the specific position ll.add(1, "D"); System.out.println("After invoking add(int index, E element) method: "+ll); LinkedList</string><string> ll2=new LinkedList</string><string>(); ll2.add("E"); ll2.add("XY"); //Adding second list elements to the first list ll.addAll(ll2); System.out.println("After invoking addAll(Collection<? extends E> c) method: "+ll); LinkedList</string><string> ll3=new LinkedList</string><string>(); ll3.add("ABC"); ll3.add("DEF"); //Adding second list elements to the first list at specific position ll.addAll(1, ll3); System.out.println("After invoking addAll(int index, Collection<? extends E> c) method: "+ll); //Adding an element at the first position ll.addFirst("UVW"); System.out.println("After invoking addFirst(E e) method: "+ll); //Adding an element at the last position ll.addLast("Z"); System.out.println("After invoking addLast(E e) method: "+ll); } } </string> |
Output:

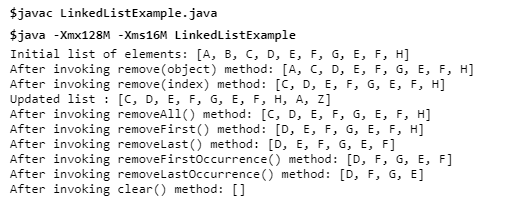
Example: Different ways to remove an element:
import java.util.*; import java.util.*; public class LinkedListExample{ public static void main(String [] args) { LinkedList<string> ll=new LinkedList</string><string>(); ll.add("A"); ll.add("B"); ll.add("C"); ll.add("D"); ll.add("E"); ll.add("F"); ll.add("G"); ll.add("E"); ll.add("F"); ll.add("H"); System.out.println("Initial list of elements: "+ll); //Removing specific element from arraylist ll.remove("B"); System.out.println("After invoking remove(object) method: "+ll); //Removing element on the basis of specific position ll.remove(0); System.out.println("After invoking remove(index) method: "+ll); LinkedList</string><string> ll2=new LinkedList</string><string>(); ll2.add("A"); ll2.add("Z"); // Adding new elements to arraylist ll.addAll(ll2); System.out.println("Updated list : "+ll); //Removing all the new elements from arraylist ll.removeAll(ll2); System.out.println("After invoking removeAll() method: "+ll); //Removing first element from the list ll.removeFirst(); System.out.println("After invoking removeFirst() method: "+ll); //Removing first element from the list ll.removeLast(); System.out.println("After invoking removeLast() method: "+ll); //Removing first occurrence of element from the list ll.removeFirstOccurrence("E"); System.out.println("After invoking removeFirstOccurrence() method: "+ll); //Removing last occurrence of element from the list ll.removeLastOccurrence("F"); System.out.println("After invoking removeLastOccurrence() method: "+ll); //Removing all the elements available in the list ll.clear(); System.out.println("After invoking clear() method: "+ll); } } </string> |
Output:
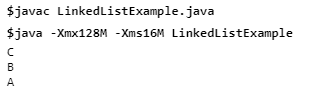
Example: To reverse a list of elements:
import java.util.*; public class LinkedListExample{ public static void main(String args[]){ LinkedList<string> ll=new LinkedList</string><string>(); ll.add("A"); ll.add("B"); ll.add("C"); //Traversing the list of elements in reverse order Iterator i=ll.descendingIterator(); while(i.hasNext()) { System.out.println(i.next()); } } } </string> |
Output: