TreeMap:
TreeMap extends AbstractMap class and implements the NavigableMap interface. It contains the elements in key-value pair form. It maintains ascending order for its elements. It is not allowed duplicate keys.
Note:
- A TreeMap can have only one null key but can have multiple null values.
- It is non-synchronized.
TreeMap class declaration:
public class TreeMap<K,V> extends AbstractMap<K,V> implements NavigableMap<K,V>, Cloneable, Serializable
Where:
- K: The type of keys maintained by the TreeMap.
- V: The type of mapped values.
TreeMap class Constructors:
| Constructor | Description |
| TreeMap() | It will create an empty treemap that will be sorted using the natural order of its key. |
| TreeMap(Comparator<? super K> comparator) | It will create an empty tree-based map that will be sorted using the comparator comp. |
| TreeMap(Map<? extends K,? extends V> m) | It will create and initialize a treemap with the entries from m, which will be sorted using the natural order of the keys. |
| TreeMap(SortedMap<K,? extends V> m) | It will create and initialize a treemap with the entries from the SortedMap m, which will be sorted in the same order as m. |
TreeMap class Methods:
| Method | Description |
| Map.Entry<K,V> ceilingEntry(K key) | It will return the key-value pair having the least key, greater than or equal to the specified key, or null if there is no such key. |
| K ceilingKey(K key) | It will return the least key, greater than the specified key or null if there is no such key. |
| void clear() | It will eliminate or delete all the key-value pairs from a map. |
| Object clone() | It will return a shallow copy of TreeMap instance. |
| Comparator<? super K> comparator() | It will return the comparator that arranges the key in order, or null if the map uses the natural ordering. |
| NavigableSet<K> descendingKeySet() | It will return a reverse order NavigableSet view of the keys contained in the map. |
| NavigableMap<K,V> descendingMap() | It will return the specified key-value pairs in descending order. |
| Map.Entry firstEntry() | It will return the key-value pair having the least key. |
| Map.Entry<K,V> floorEntry(K key) | It will return the greatest key, less than or equal to the specified key, or null if there is no such key. |
| void forEach(BiConsumer<? super K,? super V> action) | It will perform the given action for each entry in the map until all entries have been processed or the action throws an exception. |
| SortedMap<K,V> headMap(K toKey) | It will return the key-value pairs whose keys are strictly less than toKey. |
| NavigableMap<K,V> headMap(K toKey, boolean inclusive) | It will return the key-value pairs whose keys are less than (or equal to if inclusive is true) toKey. |
| Map.Entry<K,V> higherEntry(K key) | It will return the least key strictly greater than the given key, or null if there is no such key. |
| K higherKey(K key) | It will return true if this map contains a mapping for the specified key. |
| Set keySet() | It will return the collection of keys that exist on the map. |
| Map.Entry<K,V> lastEntry() | It will return the key-value pair having the greatest key, or null if there is no such key. |
| Map.Entry<K,V> lowerEntry(K key) | It will return a key-value mapping associated with the greatest key strictly less than the given key, or null if there is no such key. |
| K lowerKey(K key) | It will return the greatest key strictly less than the given key, or null if there is no such key. |
| NavigableSet<K> navigableKeySet() | It will return a NavigableSet view of the keys contained in this map. |
| Map.Entry<K,V> pollFirstEntry() | It will eliminate and return a key-value mapping associated with the least key in this map, or null if the map is empty. |
| Map.Entry<K,V> pollLastEntry() | It will eliminate and return a key-value mapping associated with the greatest key in this map, or null if the map is empty. |
| V put(K key, V value) | It will add the specified value with the specified key in the map. |
| void putAll(Map<? extends K,? extends V> map) | It will copy all the key-value pairs from one map to another map. |
| V replace(K key, V value) | It will replace the specified value for a specified key. |
| boolean replace(K key, V oldValue, V newValue) | It will replace the old value with the new value for a specified key. |
| void replaceAll(BiFunction<? super K,? super V,? extends V> function) | It will replace each entry’s value with the result of invoking the given function on that entry until all entries have been processed or the function throws an exception. |
| NavigableMap<K,V> subMap(K fromKey, boolean fromInclusive, K toKey, boolean toInclusive) | It will return key-value pairs whose keys range from fromKey to toKey. |
| SortedMap<K,V> subMap(K fromKey, K toKey) | It will return key-value pairs whose keys range from fromKey, inclusive, to toKey, exclusive. |
| SortedMap<K,V> tailMap(K fromKey) | It will return key-value pairs whose keys are greater than or equal to fromKey. |
| NavigableMap<K,V> tailMap(K fromKey, boolean inclusive) | It will return key-value pairs whose keys are greater than (or equal to, if inclusive is true) fromKey. |
| boolean containsKey(Object key) | It will return true if the map contains a mapping for the specified key. |
| boolean containsValue(Object value) | It will return true if the map maps one or more keys to the specified value. |
| K firstKey() | It will return the first (lowest) key currently in this sorted map. |
| V get(Object key) | It will return the value to which the map maps the specified key. |
| K lastKey() | It will return the last (highest) key currently in the sorted map. |
| V remove(Object key) | It will eliminate or delete the key-value pair of the specified key from the map. |
| Set<Map.Entry<K,V>> entrySet() | It will return a set view of the mappings contained in the map. |
| int size() | It will return the number of key-value pairs that exist in the hashtable. |
| Collection values() | It will return a collection view of the values contained in the map. |
TreeMap example:
TreeMapTest.java
import java.util.Iterator; import java.util.Map; import java.util.Set; import java.util.TreeMap; /** * This class is used to show the TreeMap functionality. * @author w3schools */ public class TreeMapTest { public static void main(String args[]){ //Create TreeMap object. Map treeMap = new TreeMap(); //Add objects to the TreeMap. treeMap.put(4, "Roxy"); treeMap.put(2, "Sunil"); treeMap.put(5, "Sandy"); treeMap.put(1, "Munish"); treeMap.put(3, "Pardeep"); //Print the TreeMap object. System.out.println("TreeMap elements:"); System.out.println(treeMap); //Get iterator Set set=treeMap.entrySet(); Iterator iterator=set.iterator(); //Print the TreeMap elements using iterator. System.out.println("TreeMap elements using iterator:"); while(iterator.hasNext()){ Map.Entry mapEntry=(Map.Entry)iterator.next(); System.out.println("Key: " + mapEntry.getKey() + ", " + "Value: " + mapEntry.getValue()); } } } |
Output:
TreeMap elements: {1=Munish, 2=Sunil, 3=Pardeep, 4=Roxy, 5=Sandy} TreeMap elements using iterator: Key: 1, Value: Munish Key: 2, Value: Sunil Key: 3, Value: Pardeep Key: 4, Value: Roxy Key: 5, Value: Sandy |
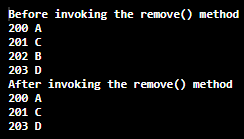
TreeMap Example: remove():
import java.util.*; public class TreeMapExample{ public static void main(String args[]) { TreeMap<Integer,String> map=new TreeMap<Integer,String>(); map.put(200,"A"); map.put(202,"B"); map.put(201,"C"); map.put(203,"D"); System.out.println("Before invoking the remove() method"); for(Map.Entry m:map.entrySet()) { System.out.println(m.getKey()+" "+m.getValue()); } map.remove(202); System.out.println("After invoking the remove() method"); for(Map.Entry m:map.entrySet()) { System.out.println(m.getKey()+" "+m.getValue()); } } } |
Output:
NavigableMap Example:
import java.util.*; public class TreeMapExample{ public static void main(String args[]){ NavigableMap<Integer,String> map=new TreeMap<Integer,String>(); map.put(200,"A"); map.put(202,"B"); map.put(201,"C"); map.put(203,"D"); //Maintains descending order System.out.println("descendingMap: "+map.descendingMap()); //Returns key-value pairs whose keys are less than or equal to the specified key. System.out.println("headMap: "+map.headMap(202,true)); //Returns key-value pairs whose keys are greater than or equal to the specified key. System.out.println("tailMap: "+map.tailMap(202,true)); //Returns key-value pairs exist in between the specified key. System.out.println("subMap: "+map.subMap(200, false, 202, true)); } } |
Output:
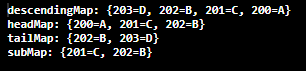
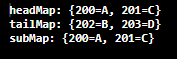
SortedMap Example:
import java.util.*; public class TreeMapExample{ public static void main(String args[]){ SortedMap<Integer,String> map=new TreeMap<Integer,String>(); map.put(200,"A"); map.put(202,"B"); map.put(201,"C"); map.put(203,"D"); //Returns key-value pairs whose keys are less than the specified key. System.out.println("headMap: "+map.headMap(202)); //Returns key-value pairs whose keys are greater than or equal to the specified key. System.out.println("tailMap: "+map.tailMap(202)); //Returns key-value pairs exist in between the specified key. System.out.println("subMap: "+map.subMap(200, 202)); } } |
Output:
Next Topic: PriorityQueue in java with example.
Previous Topic: LinkedHashMap in java with example.