- The plasma membrane (cell membrane, plasma lemma) is a thin, elastic, semi permeable living membrane found on the outer surface of all protoplasts.
- It separates the cellular protoplasm with their environment.
- The term plasma membrane was coined by Nageli and C.Cramer in 1855.
Unit membrane concept:
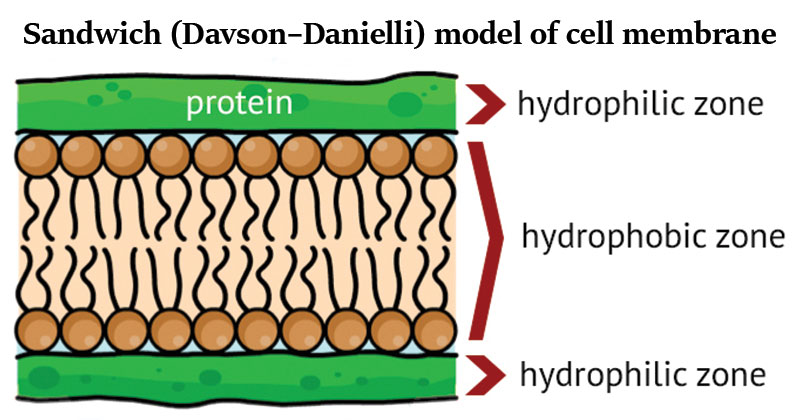
- Danielli and Davson had proposed a Sandwich Model for the plasma membrane.
- According to the concept, the plasma membrane is made up of a phospholipid layer sandwiched between two continuous layers of protein; the lipid molecules are set at right angles to the surface.
- The protein layers are hydrophilic (water loving) and the lipid layers are hydrophobic (water-fearing).
- Plasma membrane is about 75 A° in thick.
- According to Robertson all biological membranes are formed of three layers, an outer protein layer, a middle lipid layer and an inner protein layer
- Such a membrane is called unit membrane and this concept is called unit membrane concept.
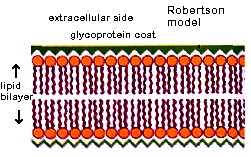
- Plasma membranes of prokaryotes and eukaryotes are unit membranes
- A number of models have been proposed to explain the structure of plasma membrane.
- Of these fluid mosaic model is the most notable one.
Fluid mosaic model:
- This model was proposed by Singer and Nicolson in 1972. They described it as ‘protein icebergs in a sea of lipids.
- According to this model the plasma membrane consists of two layers of lipids with their polar head groups towards the outside and the non-polar tails pointing inwards.
- Protein molecules are embedded among the lipid molecules.
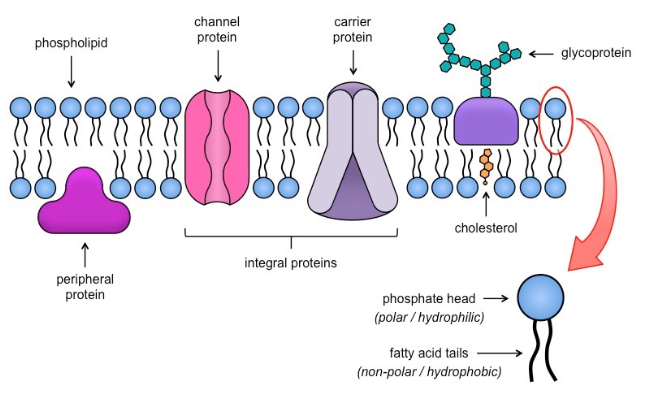
- Some large globular integral proteins which project beyond the lipid layer on both the sides are believed to have channels through which water soluble materials can pass. And they are called integral proteins.
- The peripheral proteins are loosely arranged on the outer surface (extrinsic proteins).
- There are also certain specific proteins called membrane receptors which mediate the flow of materials and information into the cell.
- The rest of the proteins are immersed in lipid bilayer (intrinsic proteins). This model is now almost universally accepted.

- Proteins are not fixed within the lipid bi-layer but are free to move like icebergs floating in the sea of lipids.
- This picture inspires the name fluid mosaic model.
Functions of plasma membrane
- lt completely envelops the protoplasm.
- It gives shape to the cell.
- It regulates the exchange of materials into and out of the cell.
- Certain cell organelles develop from plasma membrane.
- Antigen specific sites of the cells are located on the surface of the plasma membrane
- Plasma membrane of nerve fibres transmits nerve impulses.
- Plasma membrane allows free movement of water)