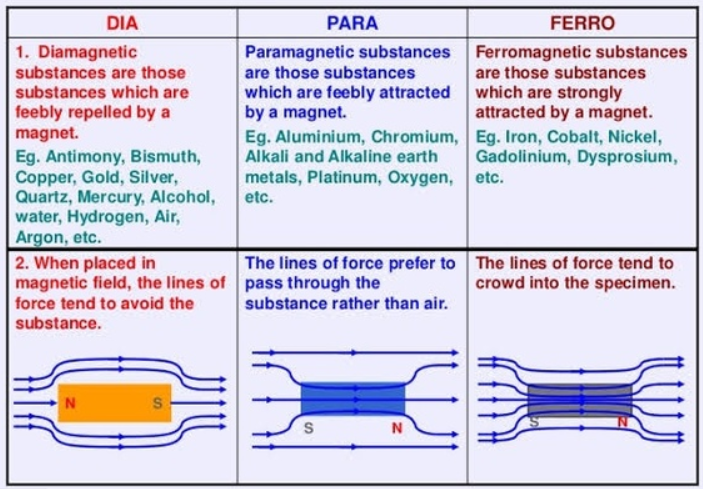
Diamagnetic Substances
These substances are weakly magnetized, when they are placed in the external magnetic field, in a direction that is opposite to the applied field. The magnetism that is exhibited by these substances is known as the diamagnetism. The examples of these substances are silver, bismuth, gold, copper, mercury, lead, air, water, nitrogen, hydrogen, silicon, and antimony.
Characteristics of Diamagnetic Substances
For every atom, the magnetic moment is zero. By the application of an external magnetic field, they are weakly repelled. By placing in the non-uniform magnetic field, their movement is from stronger to weaker parts of the field. In the external magnetic field, they are weakly magnetized, in a direction that is opposite to field.
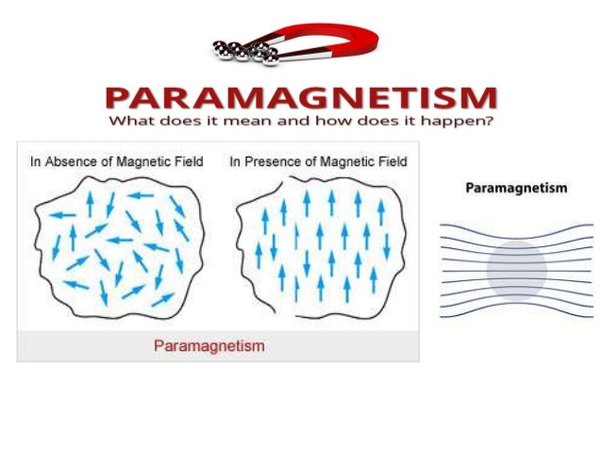
Paramagnetic Substances
These substances are weakly magnetized when they are placed in an external magnetic field, in the same direction of the applied field. Their movement is from weaker to stronger parts of the field. The magnetism that is exhibited by these substances is known as paramagnetism. The examples of these substances are chromium, calcium, sodium, manganese, aluminum, platinum, crown glass, copper chloride, oxygen, tungsten, niobium, and lithium.
Characteristics of Paramagnetic Substances
There is a magnetic dipole for every atom that causes the magnetic moment. These substances are weakly attracted by the external magnetic field. When there is the placement of these substances in the non-uniform magnetic field, then their movement is from weaker to stronger parts of the field. In the presence of the external magnetic field, they are weakly magnetized in the direction of the field. But if the external magnetic field is absent, then the magnetic moment of atomic magnets is randomly arranged. So, due to this reason, the net magnetic moment of paramagnetic substances is zero. The magnetism is lost by the removal of the external magnetic field. If the small quantity of paramagnetic liquid is contained in the watch glass, and it is placed on the two dissimilar magnetic poles, then the liquid will show an elevation in middle.
Ferromagnetic Substances
In the external magnetic field, these substances are strongly magnetized, in the direction of the externally applied field. These substances can retain the magnetic moment, even after the removal of the external field. The examples of these substances are cobalt, nickel, and iron.
Characteristics of Ferromagnetic Substances
When these substances are placed in an external magnetic field, they are strongly magnetized. They are made up of a large number of domains. If they are heated above the curie temperature, then they are converted to the paramagnetic substances. The magnetic susceptibility for these substances is large and positive.