Chemistry is a branch of science which helps us in study of matter. While studying the matter we basically look at its composition, its properties and how it changes. Anything which has mass and takes up space is called as matter i.e. anything that has physical existence. Chemistry is also sometimes referred as central science because it provides a foundation for understanding both basic and applied scientific disciplines at a fundamental level.
For example chemistry explains plant chemistry (botany), the formation and destruction of igneous rocks (geology), formation of atmospheric ozone and degradation of environmental pollutants (ecology), the nature and properties of the soil on the moon (astrophysics), Working and functions of medicines (pharmacology), and collection of DNA evidence at a crime scene (forensics ).
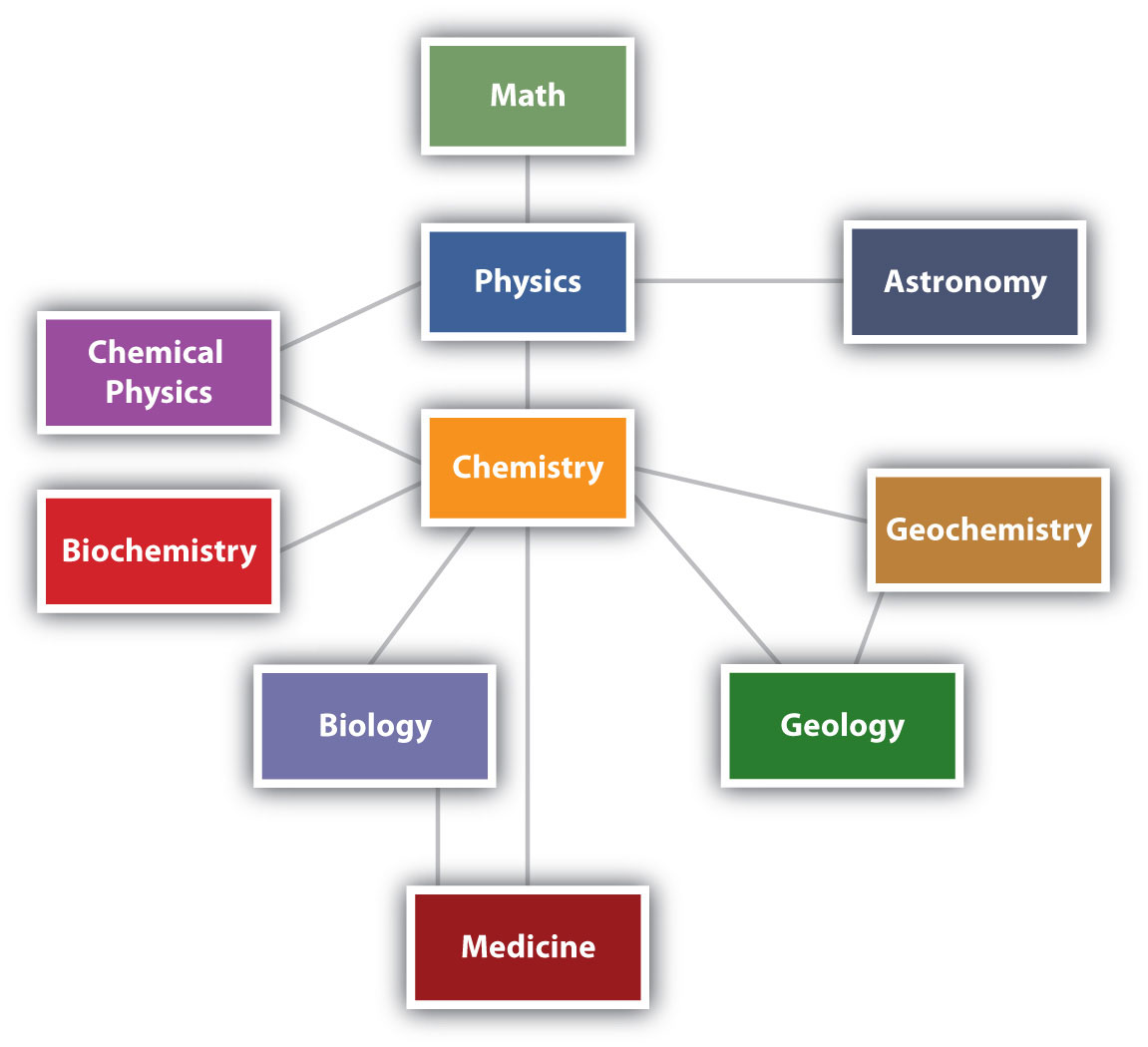
Although we have divided science into different fields, overlap among them is visible at many instances. For example, some biologists and chemists work in both fields so much that their work is called biochemistry. Similarly, geology and chemistry overlap in the field called geochemistry. Figure above shows how many of the individual fields of science are related. All of these fields at some level depend on matter because they all involve “stuff”; because of this, chemistry has been called the “central science”, linking them all together.
The study of modern chemistry can be divided into many branches. We can generally break it down into five main disciplines, or areas of study:
- Physical chemistry: It is nothing but the study of macroscopic properties, atomic properties, and phenomena in chemical systems. A chemist will study such things in the form of rates of chemical reactions, the energy transfers that occur in reactions, or the physical structure of materials at the molecular level.
- Organic chemistry: The study of chemicals containing carbon is known as Organic chemistry. Carbon is undoubtedly one of the most abundant elements on Earth and is capable of forming a tremendously vast number of chemicals. Most of the chemicals found around and in all living organisms are based on carbon.
- Inorganic chemistry: Inorganic chemistry is the study of chemicals which are in general not based on carbon. Inorganic chemicals are commonly found in rocks and minerals. One of the important area of inorganic chemistry deals with the design and properties of materials involved in energy and information technology.
- Analytical chemistry: The study of the composition of matter forms the subject matter of Analytical chemistry. It focuses on separating, identifying, and quantifying chemicals in samples of matter. An analytical chemist may use complex instruments to analyse an unknown material in order to determine its various components.
- Biochemistry: The study of chemical processes that occur in living things comes under Biochemistry. Research may cover anything from basic cellular processes up to understanding disease states so better treatments can be developed.
Many civilizations contributed to the growth of chemistry. A lot of early chemical research focused on practical uses things around us. Basic chemistry theories were developed during the nineteenth century. New materials and batteries are a few of the products of modern chemistry. Today the scope of chemistry has widened to great extent. Right from baking cake in house to nuclear reactions everything around us involves chemistry. Because of this the study of chemistry becomes very important.