Alkenes are hydrocarbons containing at least one double bond and are unsaturated. What will be the general formula of alkenes? If there is one double bond between two carbon atoms in alkenes, they should contain two hydrogen atoms less than that of alkanes. Therefore the general formula for alkenes is CnH2n. Alkenes are also known as olefins which means oil forming. This is because the first member, ethylene or ethene (C2H4) was found to form an oily liquid on reaction with chlorine
The double bond is shared by the two carbon containing elements does not involve the hydrogen atoms, althoughthis point is not made obvious by the condensed formula.It should be noted here that the molecular formula for ethene is C2H4, whereas that for ethane is C2H6.The first two alkenes ethene and propene, are ordinarily called by their common names—ethylene and propylene, (also called ethene and propene) respectively. Ethylene is one of the major commercial chemical. In US More than half of the ethylene is used the manufacture of polyethylene, one of the most familiar plastics. Propylene is also an important industrial chemical. It is converted to plastics, isopropyl alcohol, and a variety of other products.
Although there is only one alkene with the formula C2H4 (ethene) and only one with the formula C3H6 (propene), there are several alkenes with the formula C4H8.
Carbon-carbon double bond in alkenes possess one strong sigma (σ) bond (it has bond enthalpy of about 397 kJ mol–1) due to head-on overlapping of sp 2 hybridised orbitals and one weak pi (π) bond (bond enthalpy is about 284 kJ mol–1). It is obtained by lateral or sideways overlapping of the two 2p orbitals of the two carbon atoms. The double bond is shorter in bond length (134 pm) when compared with the the C–C single bond (154 pm).
Due to poor sideways overlapping between the two 2p orbitals, the pi (π) bond is a weaker. Thus, alkenes behave as sources of loosely held mobile electrons due to the presence of the pi (π) bond. Because of this, alkenes can be easily attacked by reagents or compounds which are in search of electrons. Such reagents are knows as electrophilic reagents. The presence of weaker π-bond also makes alkenes unstable molecules in comparison to alkanes. Hence, alkenes can be changed into single bond compounds by combining it with the electrophilic reagents. Strength of the double bond with bond enthalpy, 681 kJ mol–1 is greater than that of a carbon-carbon single bond in ethane of bond enthalpy, 348 kJ mol–1. Orbital diagrams of ethene molecule are shown in figure
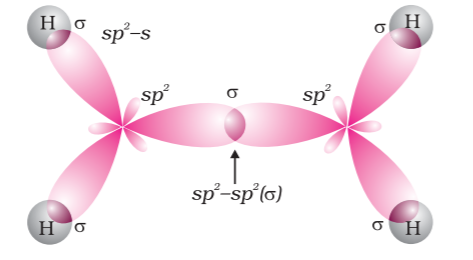
Orbital picture of ethene depicting σ bonds only
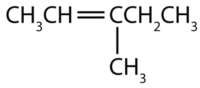
Example: Find out the structure for each compound.
3-methyl-2-pentene
Solution
First draw the parent chain of five carbon atoms: C–C–C–C–C. Then place the double bond between the second and third carbon atoms:
![]()
Nowon the third carbon atom, place the methyl group atom and add enough hydrogen atoms to give each carbon atom a total of four bonds.